Introduction:
The automotive industry has always been at the forefront of innovation, constantly driving to create safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly vehicles. In recent years, a new player has emerged that is poised to revolutionize the way cars are developed, manufactured, and even driven by Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI).
This cutting-edge technology makes substantial inroads in the global automotive sector, fundamentally altering how vehicles are conceived, built, and operated. We will explore how Generative AI is reshaping the automotive landscape across various fronts, from design and manufacturing to customer experience and sustainability.In the highly competitive world of automotive design, every ounce of innovation counts.
Generative AI has become a game-changer in this regard. AI can rapidly generate and refine design concepts by employing algorithms that mimic human designers’ creative and optimization processes. These concepts can be tweaked and modified based on various parameters, such as aerodynamics, safety, and aesthetics. This accelerates the prototyping phase and reduces design time and costs. Automakers can explore myriad design possibilities, from streamlined electric vehicles to futuristic autonomous pods, all with the help of Generative AI.
Generative AI extends its influence beyond design and into manufacturing. It assists in optimizing manufacturing processes, mainly as the industry explores advanced techniques like 3D printing. AI-driven generative design can generate toolpath strategies for complex components, reducing manufacturing time and waste. This level of Efficiency is paramount in the competitive world of automotive manufacturing. By harnessing the power of AI, automakers can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and deliver high-quality vehicles to the market. Automakers rely on efficient supply chain management to meet production demands and control costs.
Generative AI is instrumental in predicting demand, optimizing inventory, and identifying potential disruptions. AI can accurately forecast and ensure the availability of parts, enhancing supply chain resilience and minimizing production delays. Maintaining quality standards is non-negotiable in the automotive industry. Computer vision systems powered by generative AI play a vital role in quality control on the production line. These systems can swiftly detect defects and anomalies in components or finished vehicles, enabling automakers to identify issues early in manufacturing. By doing so, they can minimize costly recalls and prevent damage to their brand’s reputation. This saves money and enhances customer trust in the brand’s commitment to delivering high-quality products.
Generative AI is at the heart of the autonomous driving revolution. It is used extensively to simulate real-world driving scenarios, generate training data, and optimize control algorithms for self-driving cars. These algorithms enable vehicles to safely perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and navigate complex environments. As autonomous vehicles inch closer to becoming a reality on our roads, Generative AI is a critical enabler of this transformation, promising safer and more efficient transportation.
Generative Design in EV Manufacturing:
New product design and manufacturing approaches combine algorithms and computational design into new possibilities for the future of automotive industry. With Generative Design for car technology, designers can experiment and find new with the help of algorithms.
The core concept of (GD) is computational creativity. GD leverages computational processes to generate and evaluate design options guided by set objectives and engineering constraints. What does it mean that the technology is computational and iterative?
- GD relies on computational processes to generate and assess potential solutions. Algorithms, in combination with objectives and engineering constraints, explore the design space.
- GD is an iterative process. The output from each iteration informs the next, ensuring that the final design meets the optimal specifications.
The advancement in machine learning and artificial intelligence has impacted the field of generative design. With smarter algorithms and AI assistance, the GD process has become more capable of handling complex design problems. These improvements have also led to increased automation, allowing designers to spend more time on high-level tasks, such as evaluating and refining design options. Moreover, deep neural networks and other machine learning algorithms have opened up new avenues for GD to generate designs beyond human intuition.
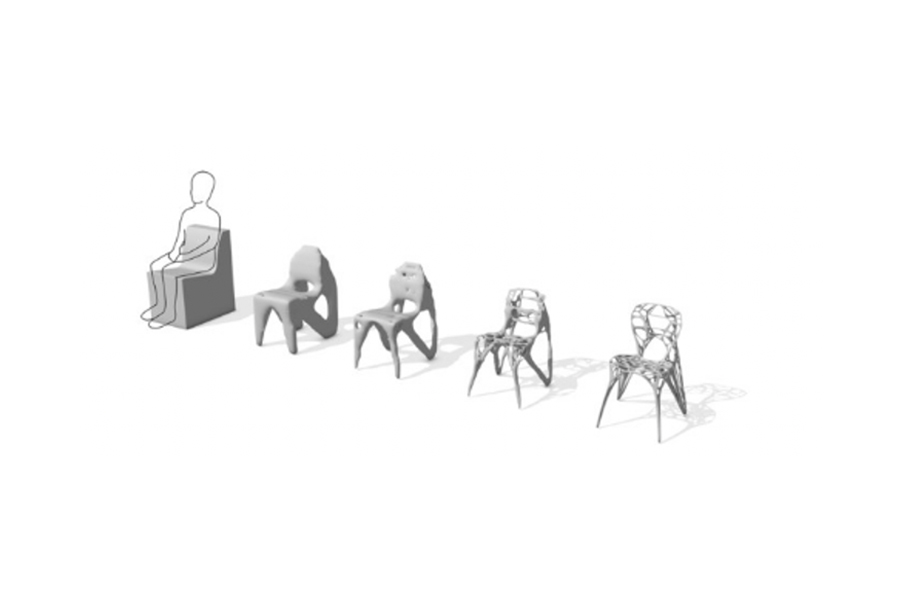
Exploration and Optimization: Topology Optimized Designs – Aesthetics of Design
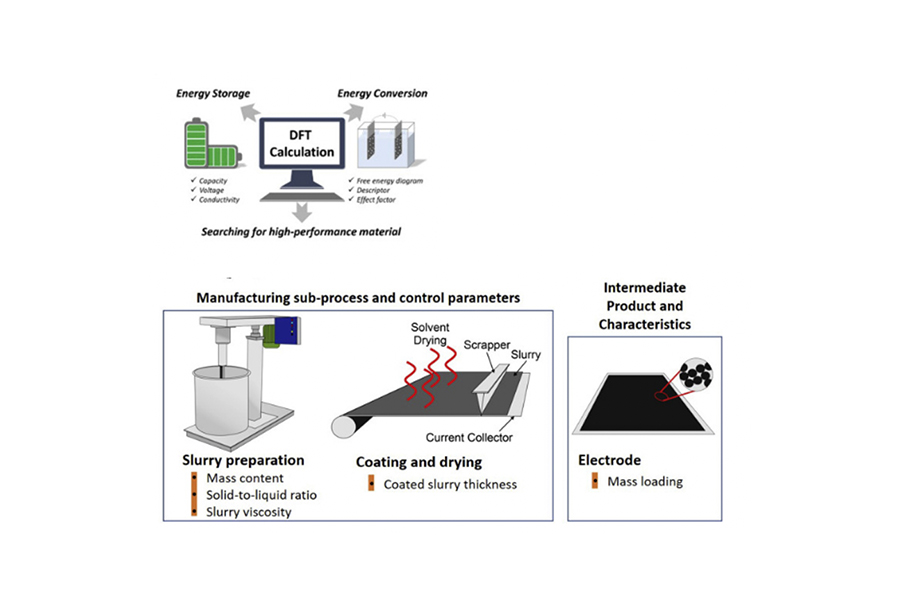
AI-Driven Battery Management:
As core components, batteries, especially lithium batteries, play an important role in providing the power source and energy storage for EVs. In an EV battery pack, individual batteries are connected and assembled into battery modules, which in turn are connected and assembled into a battery pack. The combination of series and parallel connections of the batteries within a module and the modules within a battery pack provide the desired potential and capacity.
However, current EV batteries still face performance-related issues resulting from barriers in battery design and manufacturing to battery management and optimization during operation in EVs. Limitations in battery design and manufacturing lead to lower energy density of the EV battery pack, resulting in increased cost. Additionally, more energy-efficient EV batteries can drastically alleviate user range anxiety. To achieve higher energy efficiency, consumer perception, safety, and economic feasibility, ML techniques to overcome the above challenges have received increased academic and commercial attention. By facilitating battery-material discovery, and characterizations, and improving battery-manufacturing efficiency, ML can lead the way to higher battery energy efficiency and safety and improve consumer perception of EV range.
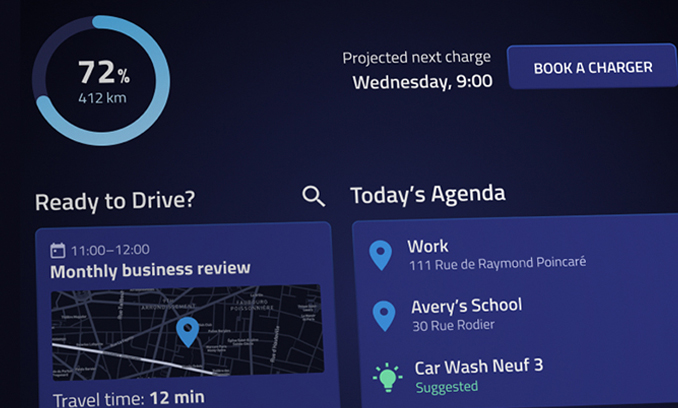
Personalized User Experience:
Personalization and customization are two terms that are often used interchangeably when they mean two different things. Personalization is when developers set up the system to deliver content, experience, or functionality that matches users’ preferences. For example, while a user is traveling, he/she will see promotions and special offers for locations they had visited before or recently searched for.
The primary goal of personalization is to deliver experiences that match specific user interests with zero effort from the targeted users. For instance, CloudMade’s system is capable of profiling the user and adjusting the interface according to the driver profile. This includes delivering personalized media, emphasizing particular information, restricting specific tools, granting access, simplifying transactions, etc. Additionally, our predictive navigation technology shows drivers the most relevant and crucial navigational information, such as traffic levels, road works, speed cameras, etc., without the user input of a destination.
The system predicts the routes drivers can take while providing useful information all throughout the journey. Automotive UX will become the differentiating factor for vehicles in the future. User Experience has its origin in the software industry, so at its core, UX is about designing solutions that satisfy customer expectations through technology. UX offers a user-centered approach for automakers to test new concepts and solutions across various offerings. Essentially, you will start by conducting UX research that will help you identify the goals and needs of your users and commonalities across target audiences. For instance, where drivers prefer to charge their vehicles and what they wish to do while waiting for their vehicles to get fully charged. Then you will create valuable products leveraging the insights you gain into user behavior.
Supply Chain Optimization:
Generative AI creates new content, such as images, text, audio or video, based on data it has been trained on. While the technology isn’t new, recent advances make it simpler to use and realize value from. As investors pour cash into the technology, executives are racing to determine the implications on operations, business models and to exploit the upside. For those who diligently pursue innovation guided by strategy and an understanding of the limitations not by an impulse to chase after the latest shiny object generative AI can prove to be an agile co-advisor and multiplier in strengthening supply chains.
What once seemed like science fiction even a year ago is now being discussed as possibilities and already being leveraged in real-world use cases across the end-to-end supply chain. These projects are enabled through generative AI’s ability to:
- Classify and categorize information based on visual or textual data
- Quickly analyze and modify strategies, plans and resource allocations based on real-time data
- Automatically generate content in various forms that enables faster response times
- Summarize large volumes of data, extracting key insights and trends
- Assist in retrieving relevant information quickly and providing instant responses by voice or text
Sustainability and Environmental Impact:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not just transforming the digital world; it’s also driving innovation in the electric vehicle (EV) sector. This article delves into how AI technologies are playing a crucial role in optimizing electric vehicle charging schedules, enhancing energy efficiency, and facilitating vehicle-to-grid (V2G) interactions. AI algorithms use historical charging data and real-time factors like electricity prices and grid load to optimize charging schedules for maximum cost-effectiveness. AI can distribute the load on the electrical grid, ensuring that charging stations operate efficiently without causing power disruptions. AI models analyze driving habits and conditions to predict an EV’s range accurately, reducing range anxiety for drivers. AI continuously assesses battery health, providing early warnings for maintenance and extending the lifespan of EV batteries. AI-driven EVs can learn from the driver’s habits and adapt charging and driving strategies for greater energy efficiency over time. AI supports fleet operators in optimizing routes, charging schedules, and maintenance, reducing operational costs and emissions.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations:
One of the most commonly quoted benefits of autonomous vehicles is that they are safer. By this, people generally mean that an AI-driven vehicle is more precise and consistent and therefore less likely to cause an accident. After all, an algorithm cannot fall asleep at the wheel, get distracted, or even drive over the speed limit. When a human driver gets into an accident, they don’t make an analytical, calculated response. They react instinctively and sometimes, essentially, randomly. There is no way of changing or controlling this response, so humans have come to accept the fact that reactions that lead to harm are simply unfortunate accidents.
As fully self-driving cars creep closer and closer to becoming a reality, many are wondering whether or not driver licenses will even be necessary anymore. Along the same lines, this brings up the question of who, or what, is responsible on the road. Could an autonomous vehicle drive a child to school with no licensed driver in the vehicle? Who is liable for damages when accidents occur on the road?
Self-driving cars have been a staple of the future for decades. However, the reality is that autonomous driving technology poses some serious ethical concerns that get left out of idealistic representations of tomorrow. Self-driving cars could very well bring a collection of incredible benefits to the world, such as mobility for those who cannot drive and time-saving opportunities for everyone.Before this can happen, though, engineers, leaders, psychologists, philosophers, and society at large must determine what moral code will be behind the computer code of our autonomous vehicles.
Future Trends and Innovations:
AI’s role in electric car management is not static. It continues to evolve, offering solutions to emerging challenges such as grid resilience, cybersecurity, and seamless V2G integration. The integration of AI into electric car management holds enormous potential. It not only enhances the user experience but also contributes to a cleaner environment and a more sustainable energy grid. AI is not limited to the vehicles themselves. It is also making inroads into mobility services like ride-sharing and autonomous driving. These applications further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of urban transportation. The future is bright for AI in electric car management. As the technology becomes more ubiquitous and sophisticated, it will not only change the way we drive but also how we interact with our vehicles, the grid, and our environment. With AI as a co-pilot, we’re navigating towards a greener and more sustainable future in the world of electric vehicles.
References:
[1] Y. Ba et al.Crash prediction with behavioral and physiological features for advanced vehicle collision avoidance system Transport. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol.(2017)
[2] M.M. Bejani et al.A context aware system for driving style evaluation by an ensemble learning on smartphone sensors data Transport. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol.(2018)
[3] S.A. Birrell et al.How driver behaviour and parking alignment affects inductive charging systems for electric vehicles Transport. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. (2015)
[4] S. Chandaka et al.Cross-correlation aided support vector machine classifier for classification of eeg signals Exp. Syst. Appl.(2009)
[5] X.M. Chen et al.Understanding ridesplitting behavior of on-demand ride services: an ensemble learning approach Transport. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. (2017)